The Adversa team makes for you a weekly selection of the best research in the field of artificial intelligence security
One of the areas of application of deep learning face recognition models is surveillance systems in public places, which require face identification. Physical adversarial attacks on such systems can be quite successful, but they require significant manipulation of the malefactor’s face, which can arouse suspicion among others. Researchers Nitzan Guetta, Asaf Shabtai, Inderjeet Singh, Satoru Momiyama and Yuval Elovici presented a novel black-box AML attack. The essence of the attack is to recreate makeup on the face of the attacker, which simultaneously prevents the system from recognizing the face and does not look suspicious.
As part of the research, the attack was tested on an ArcFace facial recognition model involving 20 people in various conditions, including angle of view, lighting, and so on. According to the results, all participants were recognized in the digital domain, however, in the physical domain, participants were recognized only in 1.22% of frames compared to 47.57%. % without makeup and 33.73% with casual natural makeup.
The method is interesting for further study, as new opportunities to conduct adversarial attacks invisible to others with high efficiency.
A great number of research has been devoted to researching the security of deep neural networks, and it has been proven that they are susceptible to adversarial attacks. While many efforts have been made to secure image classification networks, there is still a problem with video-based model protection.
The new Pseudo-Adversarial Training (PAT) algorithm was introduced by researchers Nupur Thakur and Baoxin Li. It can detect hostile frames in a video without knowing about the attack.
As part of the algorithm, “transitional frames” are generated that record the critical deviation from the original frames, and components that are insignificant for the detection problem are calculated. At the same time, “pseudo perturbations” are made to train the detection network, and therefore it is not necessary to know the attack model. As a result, hostility detection is achieved through the use of detected frames. Experiments were carried out on UCF-101 and 20BN-Jester datasets, and it has been proven that PAT can detect hostile video frames and video with a high efficiency.
A huge amount of data is now becoming available supporting the significant growth of artificial intelligence including deep learning in various applications. Despite the fact that data sources are actively used for the development of smart systems, this situation can critically affect security.
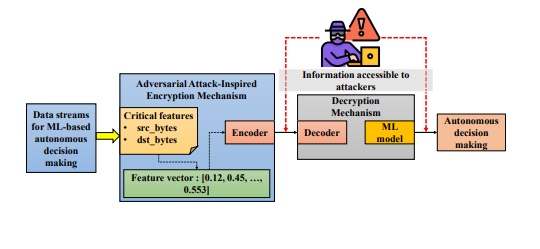
To solve the problem of data security, researchers Praveen Fernando and Jin Wei-Kocsis have introduced a new method of data encryption. The method is called AdvEncryption and uses the principle of adversarial attacks.
Although the new method is not designed to prevent illegal use of the dataset, it is capable of luring attackers into a trap by extracting deceptive data. The method consists of two main components: the first is based on an adversarial attack, an encryption mechanism to encrypt data using a covert hostile perturbation, and the second is a decryption mechanism that minimizes the impact of perturbations on the efficiency of autonomous operation. In addition, researchers provide performance data for our proposed AdvEncryption method based on case studies examining various scenarios.